Building tools for trustworthy AI systems
The project
TUPLES (TrUstworthy Planning and scheduling with Learning and ExplanationS) has built trusted planning and scheduling systems that are safe, robust, explainable and efficient
The overall aim of TUPLES has been to respond to these guidelines, by providing such foundations, approaches and tools in a particularly relevant area of AI research and applications: planning and scheduling (P&S).
TUPLES (TrUstworthy Planning and scheduling with Learning and ExplanationS) is a 3-year project that has contributed to a more integrated and human-centered approach to the development of P&S tools, in order to increase confidence in these systems and accelerate their adoption.
We have enhanced the capacity of scalable, yet transparent, robust and safe algorithmic solutions for planning & scheduling, by designing methods that combine the power of data-driven and knowledge-based symbolic AI.
TUPLES has released several tools: software applications, a simulation environment (the Tuples Lab), an implementation of the algorithms (Scikit Environment) developed in the project, and a self-assessment tool to evaluate the trustworthiness of a planning and scheduling application. Check them in the Toolkit section.
Tuples delivered on its three core objectives
First objective was to develop hybrid planning and scheduling methods that combine the efficiency, flexibility, and adaptability of data-driven learning approaches with the robustness, reliability, and explainability of model-based reasoning methods. This has required the ability to integrate learned models into the core of existing planning and scheduling approaches that rely on constraint satisfaction, combinatorial optimization, and heuristic search algorithms.
The second objective was to develop verification and explanation methods capable of reasoning about the properties of the solutions produced by planning and scheduling systems, in particular when these are represented by neural networks. Planning requires explaining plans, i.e. sequences of decisions that interact and affect possible futures, which is much more difficult.
Finally the third goal was to demonstrate these approaches on our five case studies:
- Aircraft manufacturing,
- Aircraft flying assistance
- Soccer team recruitment
- Waste collection
- Energy planning
Consortium
TUPLES involved five leading AI laboratories (ANITI, KU Leuven, Unibo, Saarland University, CVUT) and top scientists (including 2 AAAI fellows and 2 EurAI fellows) in planning & scheduling, explanations and knowledge representation & reasoning, constrained optimisation, and hybrid AI.
It also involved Social Sciences and Humanities (SSH) researchers with backgrounds as diverse as law, philosophy, human factors and psychology, who will drive some of the research, evaluation and guidelines development.
Core to TUPLES were three small and large companies (Airbus, Optit, SciSports) developing cutting-edge AI DSS in several important industry sectors: manufacturing, aviation, energy, waste transport, sport management.
Name | Legal Name | Country |
|---|---|---|
ANITI | Communaute d’Université et d’etablissements Université Federale de Tolouse Mid-Pyrenees | France |
KU Leuven | Katholieke Universiteit Leuven | Belgium |
Saarland University – UdS | Universität des Saarlandes | Germany |
UNIBO | Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna | Italy |
CVUT | České vysoké učení technické v Praze | Czech Republic |
AIRBUS | AIRBUS | France |
OPTIT srl | OPTIT srl | Italy |
SciSports B.V | SciSports B.V | Netherlands |
AIRBUS OPS LTD. | AIRBUS Operation Limited | United Kingdom |
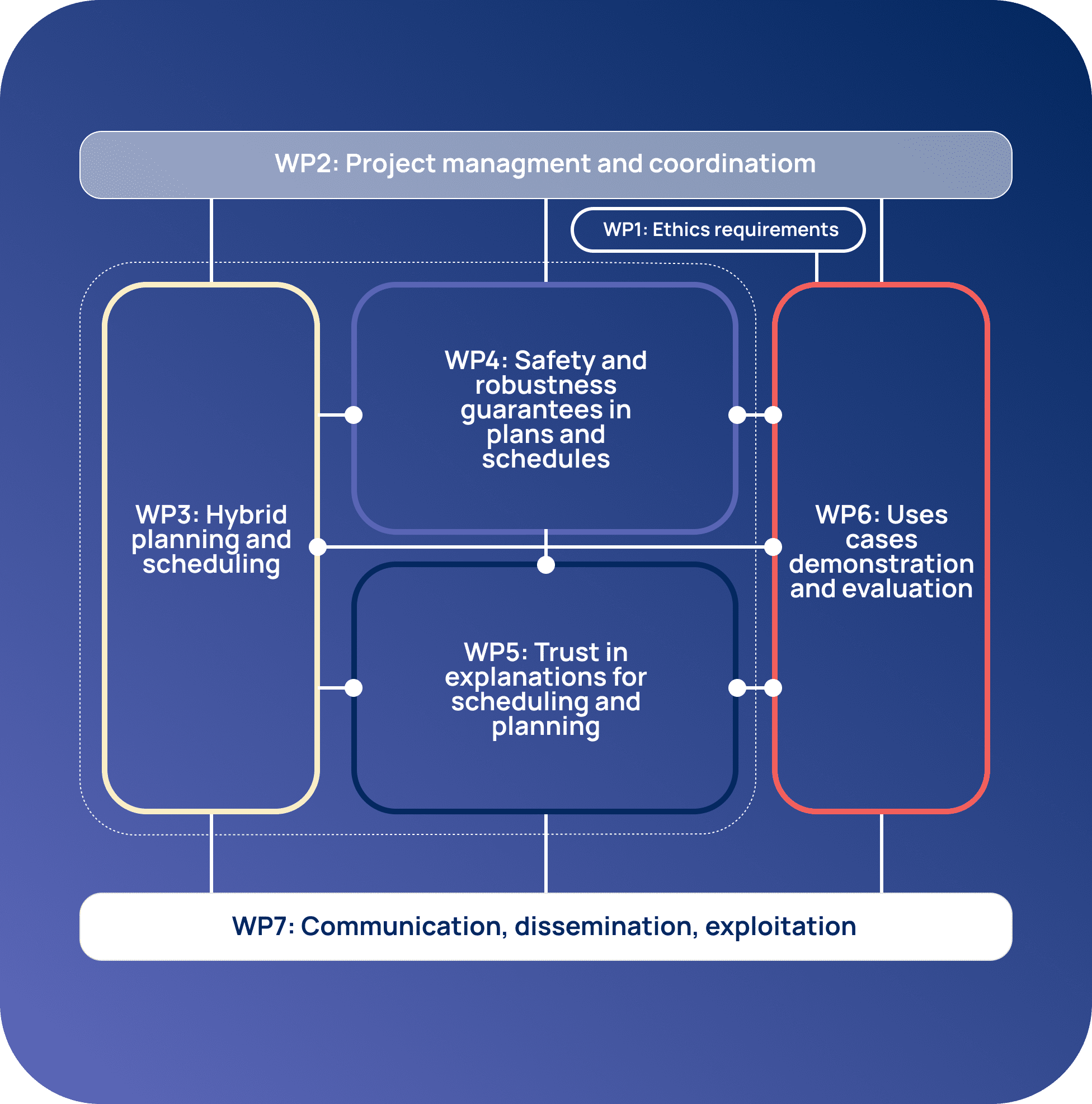
Work Packages
WP1 ensured the ethical review of the project.
WP2 dealt with the technical and administrative coordination of the project.
- In WP3, new hybrid planning and scheduling methods have been investigated, which enabled the integration of learnt and expert knowledge about the P&S problem, and facilitated the verification and explanation of the solution in WP4 and WP5.
- WP4 focused on the design of new efficient methods for guaranteeing a priori, and for verifying or testing a posteriori, the robustness and safety of the solution plans, policies, and schedules against both symbolic and learnt environment models.
- WP5 targeted new, efficient and interactive methods for explaining the solutions produced by hybrid planners, and the legal and ethical aspects of such explanations.
In WP6 the novel methods, developed in WP3-5, have been implemented and demonstrated on our 5 use-cases, and evaluated with our target properties (robustness, safety, transparency, scalability, human agency, environmental and societal well-being).
WP6 experience has been useful to derive practical guidelines concerning the design and development of trustworthy P&S systems, and for the development of TUPLES toolkit (diagnostic tool, TUPLES lab), design the international research competition, and integrate our hybrid P&S approaches into open-source libraries and platforms.
WP7 dealt with the exploitation of the results, and organise for their wide dissemination and communication.
Methodology
- New verification and testing methods
- New explanation methods
- Use-case driven development process
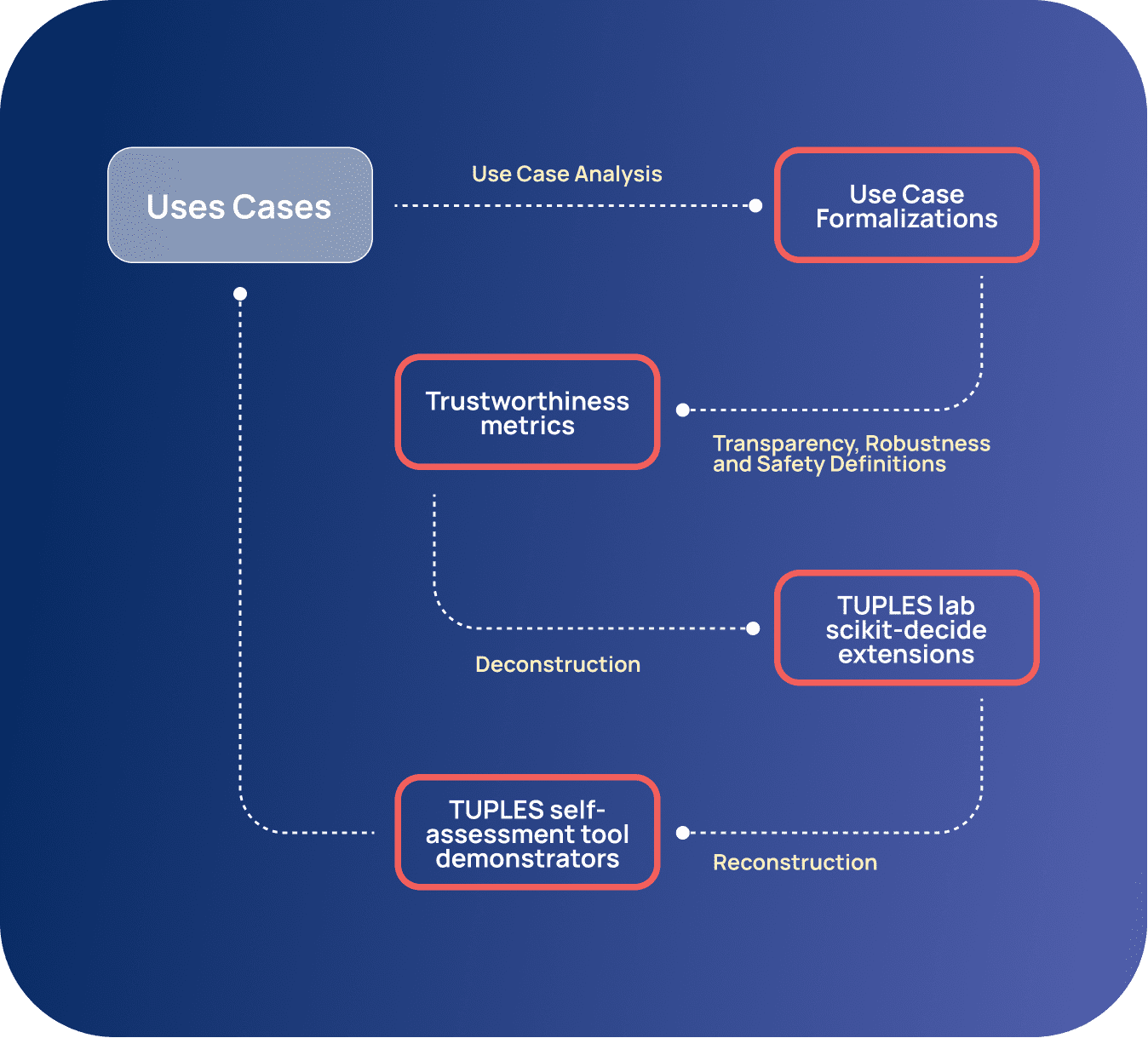
We adopted a use-case driven process aiming to provide structure to the research activities and ensure their practical viability. The process is schematically depicted in the figure, and has contributed to both usable demonstrators for the considered use cases and simplified laboratory environments suitable for controlled experiments and public release.
TUPLES has built on its industry participants’ use cases to define how and when the AI techniques developed in the project should be applied during the various stages of implementing trustworthy P&S systems.
The use cases have been selected because of their potential to contribute to progressing the state of the art, their potential of advancing the state of the practice for robust and transparent scheduling and planning systems, and their manageable risk.
With input from Human Factors and Organizational Psychology experts, the project has proposed metrics and protocols to assess and monitor the trustworthiness of the developed P&S systems, accounting for workers’ and stakeholders’ needs and opinions.
Impacts
We demonstrated these approaches on real practical case studies, from airplane pilot assistance, to soccer team recruitment, and waste collection.
The central impact of the TUPLES project lies in advancing the trustworthiness of AI, driving forward research, development, and deployment of world-class technologies that serve individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. These advancements are firmly rooted in European values, including respect for fundamental rights and a commitment to environmental sustainability.
When AI systems are designed to be safe, robust, explainable, and scalable—and are perceived as such—they can be confidently integrated into the daily practices of industries and citizens. This integration not only delivers measurable performance gains but also supports better, more informed decision-making across domains.
See also the dedicated sections of this website.
Optimal and robust P&S processes yield significant practical benefits, that can be classified across several areas:
AI-supported P&S will generally increase both efficiency and effectiveness of operations, reducing respectively the planning time and, most importantly, ensuring that models and algorithm capture the complexity of ever changing contextual conditions and recommend cost-optimal solutions, be they strategic design or operational management, supporting a general improvement in performance (which will ensure investment in AI is sustained by rapid returns).
Improved energy efficiency, reduced CO2 emissions and pollutants, lower dependence on fossil fuels and more efficient use of scarce (and costy) resources is the result of good planning in any resource- or energy-intensive process. The project includes a specific task to monitor and track environmental impacts across the 5 use cases, to provide real-life benchmarks of the potential of widespread application of AI-powered Best practices
The work environment will be positively impacted by the introduction of reliable and widely accepted P&S tools, increasing the competence, skills, and agency of human planners, foremen on the shop floor, and their workforce leading, for example, to more balanced shifts with reduced stress, limiting repetitive activities that can be performed by the AI (reducing cognitive load), and facilitating better management practices aided by explainable AI.